How to Check Folder and Sub-folders Size in Windows-
To See Which Folder is Consuming More Disk Space
Managing disk space is a common challenge for IT professionals and everyday users alike. Large folders with hidden subfolders can quickly eat up storage, and without knowing which one is the culprit, cleanup becomes difficult.
In this guide, we’ll explore multiple ways to check folder and subfolder sizes in Windows — from simple built-in methods to advanced PowerShell scripts and third-party tools.
1. The Simple and Standard Way: File Explorer Properties-
This is the quickest way to check the total size of a folder including subfolders and files.
Steps:-
- Select your folder and Press Alt + Enter Keys together.
- Or – Right click on the folder and Open Properties.
- The properties window shows the total size of the folder, including subfolders.
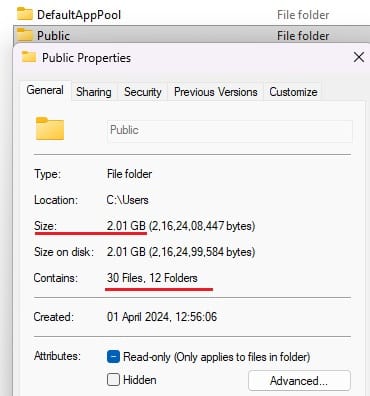
Note: If there are subfolders where you don’t have permission/access, their sizes won’t be included in above. In that case, you can try checking the folder size via the administrative share –
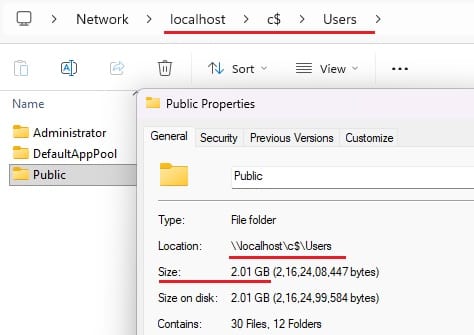
- Try to access \\localhost\c$ (replace “c” with your drive letter).
- Navigate to your folder, and check its properties again as above.

- By following the same method, you can check the size of any folder on a remote system—just change \\localhost\c$ to \\RemoteSystemNameOrIP\c$. For this you should have permission to access administrative share of remote system.
This is the quickest method to check Folder size including subfolders.
2. Using Command Prompt (CMD) - File size (Folder by Folder for subfolders)
Steps:-
- Open CMD (Recommended run as administrator).
- Run the following command: (replace C:\users\public with your folder path)
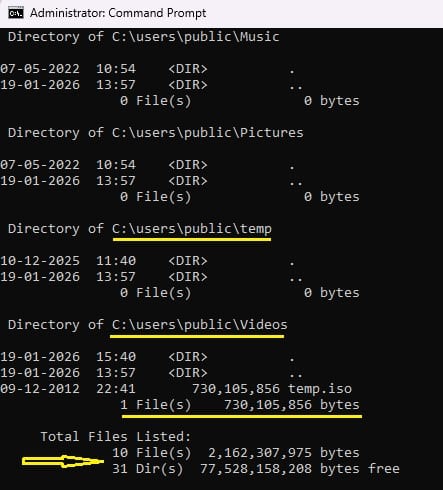
dir “C:\users\public” /s - Output will be as –

This will display total file count and size in bytes. Switch /s lists all files in the folder and its sub-folders. It has limitation to shows file sizes individually, doesn’t show folder or sub-folders size.
3. Using PowerShell: Total Size + Subfolder Sizes in MB & GB
PowerShell provides a more powerful and flexible way to calculate folder and sub-folder sizes.
Steps:-
- Open PowerShell ISE with administrator rights.
- Paste the following script in Powershell script box. (replace the path C:\users\public with your folder path.
param(
[string]$FolderPath = "C:\users\public" # Replace with your folder path.
)
if (-not (Test-Path $FolderPath)) {
Write-Host "Folder path does not exist: $FolderPath"
exit
}
$totalSize = (Get-ChildItem $FolderPath -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue |
Measure-Object -Property Length -Sum).Sum
Write-Host "Folder: $FolderPath"
Write-Host ("Total Size: {0:N2} MB ({1:N2} GB)" -f ($totalSize / 1MB), ($totalSize / 1GB))
Write-Host "-------------------------------------------"
Get-ChildItem $FolderPath -Directory | ForEach-Object {
$subSize = (Get-ChildItem $_.FullName -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue |
Measure-Object -Property Length -Sum).Sum
"{0,-40} {1,15:N2} MB ({2,10:N2} GB)" -f $_.FullName, ($subSize / 1MB), ($subSize / 1GB)
}
3. Run the script.
4. Output will be as –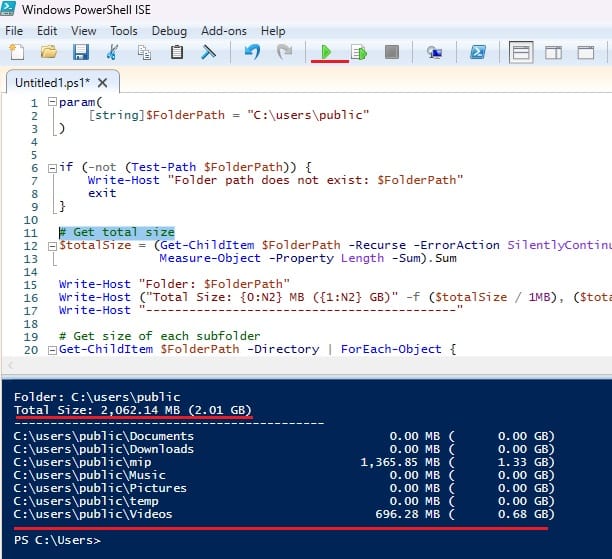
It will give the total folder size and a breakdown of each subfolder in MB and GB as above.
4. Using PowerShell: Subfolder Sizes with GUI Popup
This method is intended for those who prefer a GUI graphical pop‑up window instead of console output, making it easier to read for users.
Steps:-
- Open PowerShell ISE with administrator rights.
- Paste the following script in Powershell script box. (replace the path C:\users\public with your folder path.
$Folderpath='C:\Users\Public' # Replace with your folder path.
$dataColl = @()
gci -force $Folderpath -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | ? { $_ -is [io.directoryinfo] } | % {
$len = 0
gci -recurse -force $_.fullname -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | % { $len += $_.length }
$foldername = $_.fullname
$foldersize= '{0:N2}' -f ($len / 1Gb)
$dataObject = New-Object PSObject
Add-Member -inputObject $dataObject -memberType NoteProperty -name “foldername” -value $foldername
Add-Member -inputObject $dataObject -memberType NoteProperty -name “foldersizeGb” -value $foldersize
$dataColl += $dataObject
}
$dataColl | Out-GridView -Title “Size of subdirectories”
3. Run the script.
4. Output will be as –
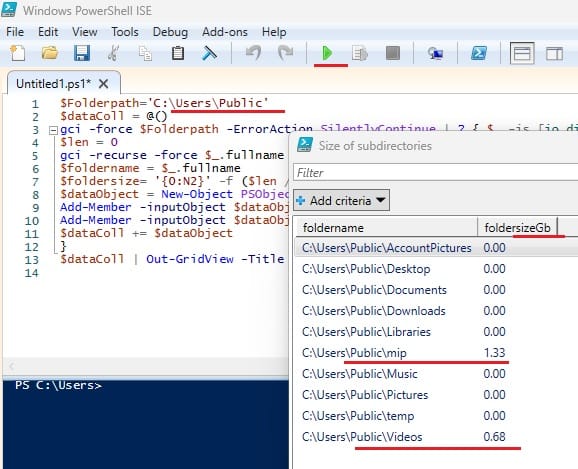
It will give a breakdown of each subfolder in GB with a GUI popup window as above.
5. Third-Party Applications: For Folder and Subfolder Size
There are several tools available for more visual breakdown and these are especially useful when you need to quickly identify large folders across an entire drive.
Few are as –
By following the any of these suitable methods, you can easily identify which folders are consuming the most disk space and take action to free up storage.



I was looking for same type PowerShell script.
Thanks.